AI enabled tools and platforms offer the potential to leverage unstructured digital information to improve customer experiences and drive business outcomes.
AI is not a silver bullet, but it is a useful tool when applied to the right use cases. This article introduces an approach for selecting AI use cases and balancing risks and rewards.
ServiceXRG defines and presents 20 possible AI for Support use cases. The dimensions for choosing which use cases to consider are described in detail following the figure.
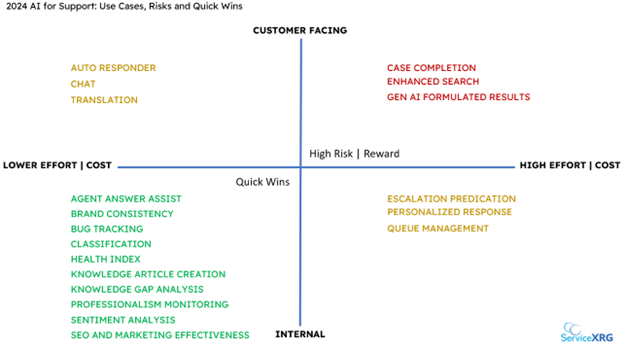
Use Case Dimensions: Customer Facing vs. Internal
AI-enabled tools can be provided to end customers or limited to internal team access. Opportunities and risk factors for internal versus external uses cases are considered below.
Internal
+ Ability to expose organizational knowledge to internal staff resulting in faster time to expertise.
+ Generative capabilities quickly create answers to share with customers.
+ Ability to maintain data privacy and security.
+ Low exposure of risk due to hallucinations and unexpected performance.
+ Ability to control use of tools.
+ Easier to capture feedback.
– Customers continue to rely on assisted channels.
– Support team may be reluctant to use AI-assisted tools.
External
+ Ability to share organizational knowledge with customers, lowering reliance on assisted resources.
+ Generative capabilities dynamically create audience appropriate responses.
+ Potential to lower cost of knowledge curation and management.
– Increased exposure to hallucinations and unexpected performance.
– Sensitive data may be inadvertently used and shared.
– Difficult to track effectiveness.
Use Case Dimensions: Level of Effort
AI-enabled tools are relatively new to the market. Many vendors report offering turnkey solutions, yet some may not be fully vetted. Considerations for the level of effort and cost to implement AI use cases are listed below.
Low Effort | Low Cost
- Out of the box extensions to the existing technology stack may offer faster deployment and lowest cost to implement.
- Low rework of data can keep deployment time and costs lower.
- Look for low administrative overhead.
- Avoid specialized skills or additional staffing for the administration of tools to keep costs lower.
- Low/no customized development.
High Effort | High Cost
- More advanced, feature rich capabilities may require longer lead times to deploy.
- Systems that require customization can cost more and take longer to deploy.
- Tools requiring new or expanded staff roles.
- Use cases that require data conversion of existing content.
- Customer facing applications require more testing.
20 AI Use Cases for Support
AGENT ANSWER ASSIST – Creation of a suggested technical response to customer questions to be used by agent (internal).
AUTO RESPONDER – AI generated response to digital customer communications (customer facing).
BRAND CONSISTENCY – Ability to generate suggested responses to customers that are consistent with core company messaging and branding (internal).
BUG TRACKING – Means to analyze case records and customer generated content to identify possible root causes of top bugs (internal).
CASE COMPLETION – Ability to suggest required data to add to a case as an electronic case is being created by the customer (customer facing).
CHAT – Intelligent chatbot to provide answers to customer questions or route to best qualified resources (customer facing).
CLASSIFICATION – Classification of unstructured digital customer information into defined categories (internal).
ENHANCED SEARCH – Use of Large Language Model (LLM) and Natural Language Query Processing (NLP) to help identify the best answer to a customer question (customer facing | internal).
ESCALATION PREDICATION – Ability to identify cases that will likely require escalation (internal).
GEN AI FORMULATED RESULTS – On demand creation of an article to answer specific customer questions (customer facing).
GRAMMER GUIDANCE – Means to improve the level of digital communication with customers by providing recommendations to improve the syntax and diction of external communication (internal).
HEALTH INDEX – Analysis of cumulative customer data to determine the status of a customer relationship (internal).
KNOWLEDGE ARTICLE CREATION – Generative capabilities used to create new knowledge base articles from exiting digital data including community posts, case records, or chat sessions (internal).
KNOWLEDGE GAP ANALYSIS – Determination of the information gaps that exist between the knowledge base and submitted case records (internal).
PERSONALIZED RESPONSE – AI generated response to customer inquiry leveraging all known information about the existing customer relationship (customer facing).
PROFESSIONALISM MONITORING – Examine the level of professionalism expressed within customer communications (internal).
QUEUE MANAGEMENT – Intelligent routing of digitally submitted cases to the best qualified resources based on case contents, known customer information, and other available resources (internal).
SENTIMENT ANALYSIS – Analysis of unstructured customer data to identify levels of customer satisfaction (internal).
SEO AND MARKETING EFFECTIVENESS – Ability to optimize external customer communications posted on the support portal to increase use and effectiveness (internal).
TRANSLATION – Language translation of support cases and responses (customer facing | internal).




